Proverbs 24:3-4
(KJV): “Through wisdom is an house builded; and by understanding it is established: And by knowledge shall the chambers be filled with all precious and pleasant riches.”
(NLT): “A house is built by wisdom and becomes strong through good sense. Through knowledge its rooms are filled with all sorts of precious riches and valuables.”
(NKJV): “Through wisdom a house is built, And by understanding it is established; By knowledge the rooms are filled With all precious and pleasant riches.”
(LBLA): “Con sabiduría se edifica una casa, y con prudencia se afianza; con conocimiento se llenan las cámaras
de todo bien preciado y deseable.”
Sources:
(2) https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/security
(3) https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/020915/what-are-some-examples-preferred-stock-and-why-do-companies-issue-it.asp
(4) https://investor.bankofamerica.com/fixed-income/preferred-stock
(5) https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1099219/000119312518183434/d596081dex31.htm
(6) https://am.gs.com/en-us/advisors/funds/detail/PV105611/38149W127/goldman-sachs-access-u-s-preferred-stock-and-hybrid-securities-etf
(7) https://www.lseg.com/content/dam/ftse-russell/en_us/documents/ground-rules/ftse-goldman-sachs-us-preferred-stock-and-hybrids-index-ground-rules.pdf
(8) https://www.lseg.com/en/ftse-russell/indices/us-preferred-stock-and-hybrids
(9) https://www.dividend.com/preferred-share-dividend-stocks-etfs-and-funds/
(10) https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/what-are-preferred-dividends
(11) https://ca.rbcwealthmanagement.com/documents/1435520/1946761/A+guide+to+preferred+shares.pdf/b645e864-6840-4ba9-bac6-c9693469c414
(12) https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/participatingpreferredstock.asp
(13) https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/career-map/sell-side/capital-markets/participating-preferred-stock/
(14) https://www.investopedia.com/articles/stocks/05/052705.asp
(15) https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/preferred-stock-potential-income-tool
(16) https://www.privatebank.citibank.com/insights/managing-reinvestment-risk
(17) https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-arbitrage
(18)
(19)
(20)
(21)
(22)
What Is Preferred Stock?
The Basics:
Preferred stock is a type of security.
According to Cornell Law School, a security is a “broad type of investment[] with risks that are regulated under securities law.”
Securities can include stocks, bonds, treasury stocks, notes, debentures, futures & swaps based on securities/security indexes, and investment contracts. According to Cornell, the Securities Act of 1933 & Securities Exchange Act of 1934 considers stocks to be per se (inherently) securities.
Preferred stock is a type of equity security.
Equity securities provide a form of ownership.
Preferred stock is also a negotiable security, which means it can trade in the market, since it can be bought & sold between investors.
Preferred stocks are best known for the consistent, quarterly payment of dividends. However, some companies may choose to disperse annually or semi-annually, instead of quarterly. These consistent dividends are most likely taxable.
Unlike common stock (which can have fluctuating dividend payments, if any), preferred stockholders often receive a fixed dividend payment. The amount of this payment can be deferred–if a company hits financial trouble. However, the amount, itself, will rarely change.
While common stocks receive capital appreciation if a company grows, preferred stock owners the yield is their only return. Additionally, common stock holders typically have voting rights; whereas, preferred shareholders typically do not have voting rights.
Preferred stock tends to have a higher rate of return than many debt securities, as there is a risk that dividend payments will not occur. However, the fixed dividend income from recurring dividends can benefit those seeking a recurring income, like retirees. Since preferred stock has no date of maturity or expiration, most preferred stockholders are long-term investors.
Investors seeking growth & capital appreciation would be better investing in common stock, instead of the fixed-income preferred stock.
Who Issues Preferred Stock?
Companies issue preferred stock as an alternative way to raise money. These corporates tend to have a capital structure that includes: senior secured debt, senior debt, subordinated debt, preferred stock, and common stock.
Companies like the Royal Bank of Canada, Capital One, Wells Fargo, Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation, Bank of America, JPMorgan Chase & Co., Georgia Power Company, and MetLife offer preferred stock as of Feburary 21st, 2025.


Proverbs 24:13-14
(KJV): “My son, eat thou honey, because it is good; and the honeycomb, which is sweet to thy taste: So shall the knowledge of wisdom be unto they soul: when thou hast found it, then there shall be a reward, and thy expectation shall not be cut off.”
(ASV): “My son, eat thou honey, for it is good; And the droppings of the honeycomb, which are sweet to thy taste: So shalt thou know wisdom to be unto they soul; If thou hast found it, then shall there be a reward, And thy hope shall not be cut off.”
(NLT): “My child, eat honey, for it is good, and the honeycomb is sweet to the taste. In the same way, wisdom is sweet to your soul. If you find it, you will have a bright future, and your hopes will not be cut short.”
(LBLA): “Come miel, hijo mío, porque es buena; sí, la miel del panal es dulce a tu paladar. Sabe que así es la sabiduría para tu alma; si la hallas, entonces habrá un futuro, y tu esperanza no será cortada.”
Par Value & Dividend Payments
Many investors like receiving dividends. The dividend payments are determined partially by the par value of the preferred stock.
The par value is also known as the face value. When a stock is originally issued (on the primary market), it is typically issued at face/par value.
While the price a stock sells for on the secondary market (the market value) will change, the par value will not.
This par value (not the market value) will be utilized to determine the dividend payment alongside the dividend rate. The dividend rate is a percentage of the par value.
Unlike bonds, which typically have a par value of $1,000, preferred stock par value is typically set at $100. However, this is not always true.
Regardless of the current market value (price on the secondary market), preferred stock always pays dividends based on par, not the market value.
See the example below for more understanding . . .
Example:
Question:
Company X issues a $100 par preferred stock with a dividend rate of 3% that pays on a semi-annual basis. The preferred stock trades on the secondary market with a ***market price of $125 dollars.
What will Company X’s semi-annual dividend payment be–assuming the Board of Directors approves it–?
Answer:
3% of $100 face/par value is $3 dollars annually.
(3 divided by 2 = 1.5)
Company X splits $3 annually into two semi-annual payments of $1.50 each.
***While the market price is $125, the market price is not utilized in determining dividend payouts in this preferred stock equation.
Do Dividend Payments Always Occur?
Preferred stock owners typically receive a dividend payment on a quarterly basis. However, some dividends are given out semi-annually or annually.
While dividend payments are not legally guaranteed with preferred stock, they are very likely to occur. Still, just like common stock dividends, the Board of Directors of a company still has to approve the dividend payment. Additionally, “preferred dividends must be paid before any dividends are issued to common stockholders, making them a more secure investment” according to an article written on Nasdaq.
When a stock is issued in the primary market, the issuer must decide whether the preferred stock will be cumulative or non-cumulative (straight).
If a company must skip a cumulative dividend payment, it needs to make up for it in the future. This means dividend payments are cumulative. These missed payments have to be paid out before holders of common stock receive future dividends if the preferred stock is classified as cumulative.
Non-cumulative (straight) dividend payments would not need to be made up in the future.
In a cumulative dividend payment situation, if the company missed several years of dividend payouts to preferred shareholders, it must pay these back before paying any dividend payments to common stockholders.
| Year | Paid | Missed |
| 2022 | Full | None |
| 2023 | Partial | 10% of total payment missed |
| 2024 | Partial | 10% missed |
| 2025 | None | 100% |
| 2026 | BOD votes on a Full Payment to both common stockholders & preferred shareholders | The company will be required to makeup the missed payments of 2023, 2024, and 2025 to preferred shareholders before making any dividend payouts for 2026 to common shareholders. |
In a non-cumulative (straight) situation, if the company missed several years of dividend payouts to preferred shareholders, it does not need to pay these back before paying dividend payments to common shareholders. It only needs to pay preferred shareholders, before common shareholders, the year it plans to pay a dividend to common shareholders.
| Year | Paid | Missed |
| 2022 | Full | None |
| 2023 | Partial | 10% of total payment missed |
| 2024 | Partial | 10% missed |
| 2025 | None | 100% |
| 2026 | BOD votes on a Full Payment to both common stockholders & preferred shareholders | The company only needs to pay preferred shareholders first in 2026, then they can pay common shareholders after. The previous missed payments DO NOT need to be paid. |
Do Dividend Payments Ever Change In Preferred Stock?
The dividend payout amount can change if a issuer elects for the preferred stock to be participating. If the preferred stock is participating, dividends can increase if a company prospers & has significant earnings to report. The additional dividend payment is typically based on a predetermined condition.
This predetermined condition is often set to occur if common shareholders receive a dividend that exceeds a certain amount. Additionally, participating preferred stockholders may have an advantage over non-participating preferred shareholders & shareholders of common stock during liquidation proceedings in bankruptcy.
Participating preferred stock is often subject to a fixed minimum dividend rate, but not a maximum. The maximum will often be influenced by how profitable the issuer is.
Participating preferred stock is desirable in the market, and will likely be offered in the primary market with lower dividend rates than non-participating preferred stock.
Since the demand is high for participating preferred stock, the secondary market prices will be higher & will offer lower yields. Since issuers must pay more when they are profitable with participating preferred stock, it is primarily a benefit to stockholders.
Venture capital firms & private equity firms typically utilize participating preferred stock to hedge against higher portfolio risks when they invest.
Companies may also utilize participating preferred stock as a method of lowering a company’s average cost of capital (WACC) which in return allows to achieve a higher valuation.
Current Dividend Yield vs. Dividend Rate
Dividend Yield is the primary formula that investors & shareholders calculate their rate of return for preferred stock securities.
Current Dividend Yield formulates the current rate of return based on the current market price.
Here is an example of a preferred stock with a high annualized dividend yield (36%):
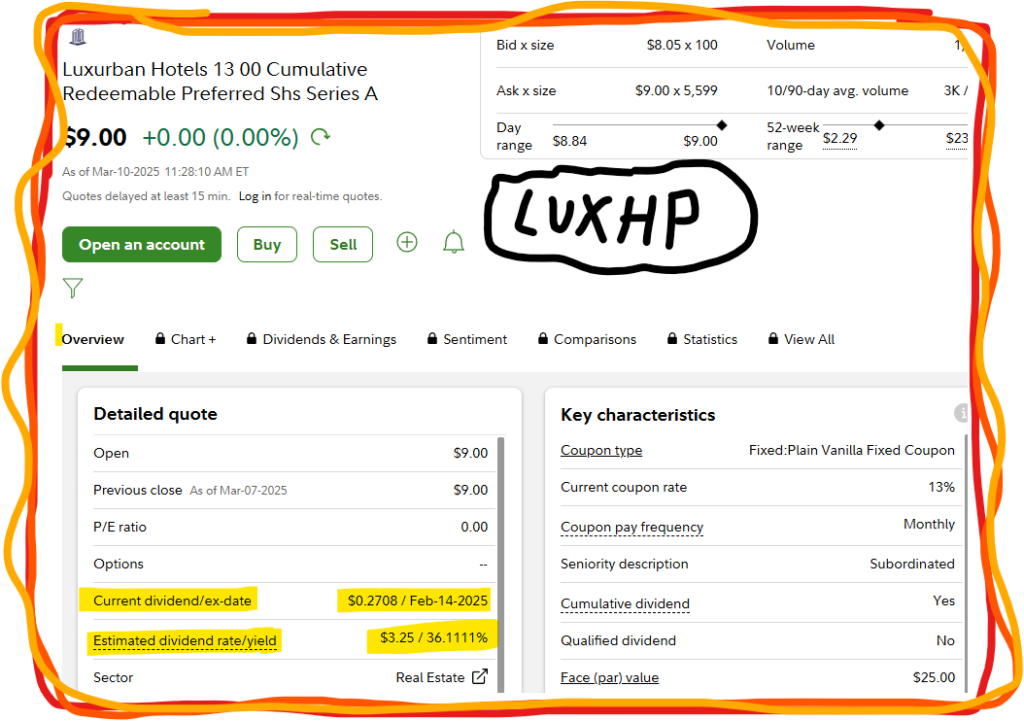
The Dividend Rate bases it’s return on par, which is issued when the preferred stock is issued on the primary market, only. Therefore, dividend rate will not be an accurate calculation of a stock’s current rate of return. Current Dividend Yield is a much more accurate formula.
Current Dividend Yield (CY) = Dividend Annual Income / Market price
CY = $10/$100
CY = 10%.
Our Current Dividend Yield(CY) is 10% based on current market price.
However, if the current market price changes, the CY will also change to reflect the change in market price.
When the CY exceeds the coupon/dividend rate, it likely trades at a discount. When the CY is lower than the coupon/dividend rate, it likely trades at a premium.
The Dividend Rate will not change once it is issued, since the dividend rate is always based on par.
Dividend Rate (DR) = Dividend Annual Income / Par
DR = $10 / $80
DR = 8%.
Our Dividend Rate is 8% and it will not fluctuate or change, as it is not based on the current market price.
Conversion Preference
Some issuers elect to have their preferred stock have a conversion option. In these instances, preferred stockholders can elect to have their preferred stock convert to common stock, which would lose it’s protecting against liquidation but provide other benefits. Here is a list of preferred stock with dividend payouts & a conversion preference.
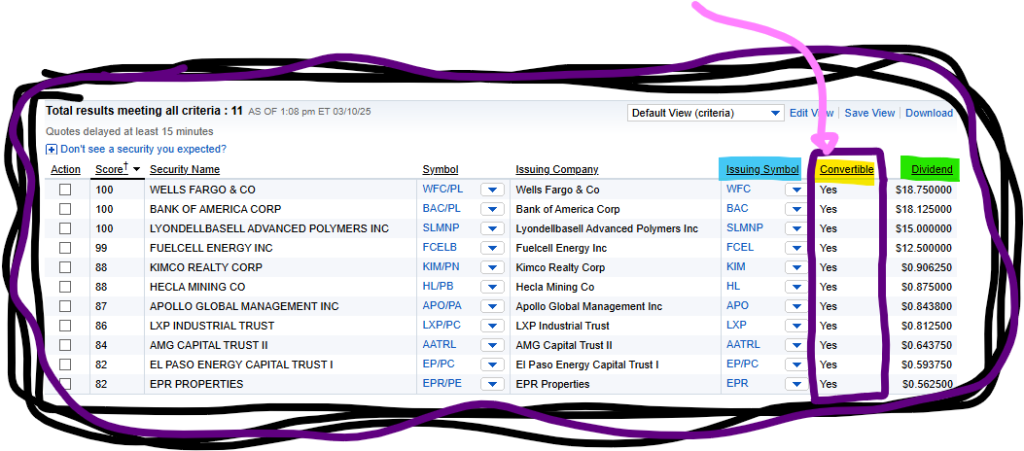
The benefit of having the preferred stock convert into common stock would be if the company grows, and the common stock value appreciates as a result. However, once converted to common stock, the former preferred stock would lose its rank in the liquidation proceedings of bankruptcy.
Additionally, the conversion ratio may differ from company to company and is set before the convertible preferred share is issued.
The benefit of a convertible preferred share is that by acting as a preferred share before it is converted, investors will likely receive a fixed dividend quarterly. Then if the company grows and the investor decides to sell for capital appreciation benefits, they can convert from a preferred stock to a common stock.
What Is Arbitrage?
Conversion can open up arbitrage opportunities.
Harvard Business School explains that “arbitrage is an investment strategy in which an investor simultaneously buys and sells an asset in different markets to take advantage of a price difference and generate a profit. While price differences are typically small and short-lived, the returns can be impressive when multiplied by a large volume.”
Example: If an investor on the secondary market buys three shares of a $100 par, 6% preferred stock with a convertible ratio of 3:1 at a price of $115 each.
Meanwhile the companies common stock is trading on the secondary market at $95 a share.
An arbitrage opportunity can exist.
If the investor paid for three preferred shares at $115 each, they would spend a total of $345 dollars.
If they converted those three preferred shares to common stock at a convertible ratio of 3:1, they would receive three shares of common stock for each preferred stock converted.
This results in a total of 9 shares of common stock.
The investor could then quickly trade these 9 shares of common stock at $95 a share for a total of $855 dollars.
This results in a total profit (without fees) of $510 dollars.
Protection Agaisnt Liquidation
Owners of preferred stock are paid before holders of common stock if a company must liquidate it’s assets during a bankruptcy proceeding.
While holders of preferred stock are still subordinate to bondholders, regarding liquidation rankings, preferred stock holders are more likely to receive some payout when compared to holders of common stock.
What Are The Downsides?
Preferred stock is given preferential treatment with cumulative dividends & liquidation, resulting in preferred stock being a safer investment than most common stocks. Preferred stock is purchased for it’s reduced risk profile & consistent income stream of dividend payouts.
However, preferred stock will likely lag behind common stock regarding capital appreciation & market value if the company grows.
A Callable Feature
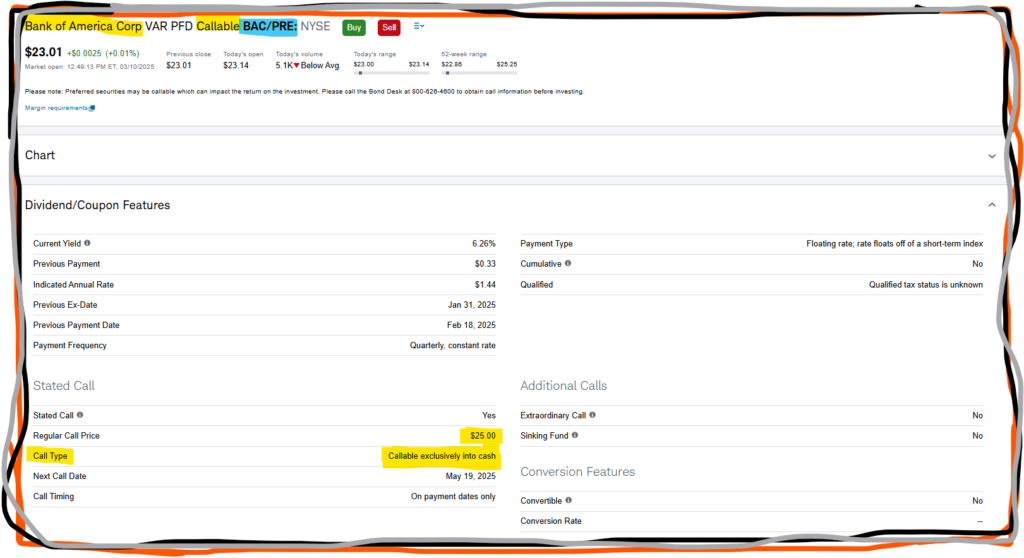
Some preferred stock is issued with a callable feature. This allows the preferred share issuer to buy back the preferred share from the investor by paying the investor the par value of the preferred stock. By calling the preferred stock, the issuer can avoid making future dividend payments & also refinance their preferred stock. The ability to refinance may depend on the dividend rate set before the stock was issued, which is influenced by market interest rates of the time.
This feature opens up investors to a “reinvestment risk”. However, some issuers offer additional call premiums & call protection.
Call premiums are an amount above the par value that the issuer must pay. Call protection is a time value that must be breached before the issuer can call the preferred share back.
Overall, due to call features benefiting the issuer, more than the investor, callable preferred shares are not as popular. Callable preferred shares are usually issued with a higher dividend rate on the primary market due to this unpopularity. Callable preferred shares may have higher yields due to their lower prices on the secondary market.
Reinvestment Risk:
A reinvestment risk occurs when an investor “will have to reinvest the coupon, principal and/or interest received from an investment at a potentially lower rate than they are currently receiving. This typically occurs when interest rates decrease during the investment horizon of an investor.”
If a company refinances their preferred stock when market interest rates are lower, the dividend rate will likely also be lower. If an individual wishes to reinvest in the new refinanced preferred stock, after their older, better-dividend paying preferred stock was called, they will likely face reinvesting with a lower yield.
Because interest rates can be influenced by the Federal Reserves actions, they can be changed rapidly.
Other Risks of Preferred Stock
Additionally, there are some key risks to consider when evaluating whether preferred stocks fit your investor risk profile: “interest rate risk, credit risk, call risk, extension risk, liquidity risk, and the risk that tax changes may negatively impact the status of dividend income.”
Additionally, preferred stock competes with bonds, since both are impacted by fluctuating interest rates.
Finally, preferred stock values may fall if the issuer of preferred stock has a decline in their financial status. This reduced financial status may impact their ability to pay dividends.
Recall consistent, quarterly dividend production is a cornerstone of investing in preferred stock.
The Impact of Interest Rates
Since preferred stock is negotiable, and can be traded amongst investors, the demand for preferred stocks will influence its market price. However, while the economy & business-related conditions can influence the market price, fluctuations in market price are primarily influenced by interest rate changes.
Since many corporations, businesses, and many of our governments utilize debt to function, interest rate changes can make it more expensive to borrow money. This can reduce a businesses’ profitability.
The market value of preferred stock has an inverse relationship with interest rates.
When interest rates rise, market prices fall.
When interest rates lower, market prices tend to rise.
There is a strong negative correlation between the market prices of preferred stock & interest rate changes.
For the most part, the economy grows when interest rates are reduced. When the interest rates are low, borrowing money to function is easier. Ideally, this additional borrowing capability allows businesses to produce goods, which should raise profitability. However, when interest rates are too low, for too long, inflation can result. Higher inflation can result when the demand for a good drives up prices. Inflation occurs when the general prices of goods & services rises more than is expected.
Fixed-income investments like preferred stock are more impacted by inflation than common stock, which can be utilized as a hedge against inflation. Typically, as inflation rises, the secondary market price for preferred stock will sink. Due to the fixed return of preferred stock, preferred stock will typically not outperform inflation.
Common stock can outperform inflation.
The Federal Reserve will also create monetary policy actions that influence interest rates. Occasionally, these monetary policy actions will have unintended results. However, announcements of a specific monetary policy action from the Federal Reserve can impact the entire market. For instance, if the Federal Reserve announces they tend to move to lower interest rates, preferred stock values may increase as a result.
Bonds:
Bonds are debt securities, where investors lend money to companies & governments, for payment at a later date. Bonds allow these corporations & governments to potentially access borrowed money at a lower interest rate than a bank loan.
Since preferred stock & bond securities both utilize par value when determining the dividend rate, investors will often compare the two securities when making an investment decision.
When interest rates rise, market prices fall. When interest rates lower, market prices tend to rise.
If the bond market can issue a higher rate of return for dividends than preferred stock, than many investors will utilize bond’s instead of preferred stock. Therefore, issuers of preferred stock should be aware of how interest rates will influence their rate of return, in comparison, to debt securities like bonds. High interest rates can make preferred stock hard to liquidate.
Unlike bonds, which typically have a par value of $1,000, preferred stock par value is typically set at $100. However, this is not always true.
Regardless, some investors may still choose to utilize preferred stock over bonds due to the familiarity of trading shares vs. trading bonds according to an article at Charles Schwab.
Decline In Finances
Finally, the liquidity of a preferred stock can be negatively impacted by a reduction in financial status of the preferred stock’s issuer. If a company is failing to profit, the Board of Directors may not issue consistent, quarterly dividends. Therefore, if this knowledge becomes known, investors may choose not to invest in that particular preferred stock, making it hard to liquidate & trade on the secondary market.
Is there an Index that follows Preferred Stock?
Yes, one main index that follows Preferred Stock is the FTSE US Preferred and Hybrids Index. The FTSE US Preferred Stock and Hyrbids Index Series “is designed to provide a performance measure of preferred stock and other hybrid instruments issued in the US and denominated in USD. Hybrid securities exhibit both bond- and equity-like features.”
Another index based on the FTSE US Preferred and Hybrids Index, is the FTSE Goldman Sachs US Preferred Stock & Hybrids Index. In fact, here is an ETF from Goldman that follows this Index.
Proverbs 24:33-34
(KJV): “Yet a little sleep, a little slumber, a little folding of the hands to sleep: So shall thy poverty come as one that travelleth; and thy want as an armed man.”
(NASB): “A little sleep, a little slumber, A little folding of the hands to rest, Then your poverty will come as a robber And your want like an armed man.”
(ESV): “A little sleep, a little slumber, a little folding of the hands to rest, and poverty will come upon you like a robber, and want like an armed man.”
(LBLA): “Un poco de dormir, un poco de dormitar, un poco de cruzar las manos para descansar, y llegará tu pobreza como ladrón, y tu necesidad como hombre armado.”

Leave a Reply