Psalm 121:1-3 (HCSB)
“I lift my eyes toward the mountains. Where will my help come from?
My help comes from the LORD, the Maker of heaven and earth.
He will not allow your foot to slip; your Protector will not slumber.”
IOS stands for Cisco Internetwork Operating System.
The Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) is an operating system that Cisco networking engineers configure/customize Cisco networking devices with. Cisco IOS is the most widely utilized network infrastructure software on the earth.
History & Creation
William Yeager, Len Bosack, Andy Bechtolsheim & Sandy Lerner all played important roles in the development of the Cisco IOS & router hardware it utilized.
Accessing the CLI
The IOS Command-Line Interface (CLI) is accessible via the console port or remotely using Secure Shell (SSH).
Typically, accessing the CLI on IOS requires the utilization of a computer.
Access Modes
Entering a question mark (?) at the router/system prompt will allow you to obtain a list of commands available for each command mode.

(1) User EXEC mode: This is the first access mode.
User EXEC mode is typically available on session start.
User EXEC mode is reserved for tasks that do NOT change the configuration of the router.
Therefore, User EXEC mode limits the availability of commands.

(2) Privileged EXEC mode: This is the second level of access.
Privileged EXEC mode typically requires a password, after entering “ENABLE” on the CLI.
Privileged EXEC mode allows for a greater list of commands than User EXEC mode.

Both User & Privileged EXEC mode commands are NOT saved across reboots of the router.
(3) Global Configuration Mode: This is the third-access level.
Global Configuration Mode allows for commands that can configure general system characteristics & make changes to the running configuration.
“Configure” is the command to enter Global Configuration mode.
Some changes can be saved, which stores them after the router reboots.

(4) Specific Configuration Modes // (5) Configuration Submodes // (6) Configuration subsubmodes
After you enter global configuration mode, you can enter “a variety of protocol-specific or feature-specific modes.”
Below configuration modes are configuration submodes, which allow the configuration of very specific features under the scope of a particular specific configuration mode.
Some of these configuration submodes, have a subsubmode below them.
These specific modes must be entered through global configuration mode.
ROM Monitor Mode
*** ROM Monitor Mode: This mode is for when the router cannot boot properly by failing to find a valid system image. Additionally, you can access this mode by interrupting the boot sequence during startup. ***
Context-Sensitive Help
Beyond using the “?” to display a list of commands for each command mode, other commands can list arguments & keywords to be utilized with specific commands.
(1) To list the next available syntax options for a specific command, utilize “commandkeyword ?”
Remember to enter a space both before & after the “commandkeyword”.
For example:

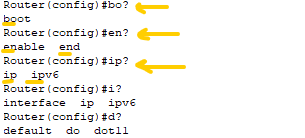
(2) Typing a partial “commandkeyword” immediately followed by a “?” with no space will show the list of potential “commandkeywords” available that can complete the partial keyword.
Psalm 121:1-8 (HCSB)
“I lift my eyes toward the mountains. Where will my help come from? My help comes from the LORD, the Maker of heaven and earth.
He will not allow your foot to slip; your Protector will not slumber. Indeed, the Protector of Israel does not slumber or sleep.
The LORD protects you; the LORD is a shelter right by your side. The sun will not strike you by day or the moon by night.
The LORD will protect you from all harm; He will protect your life. The LORD will protect your coming and going both now and forever.”


Leave a Reply